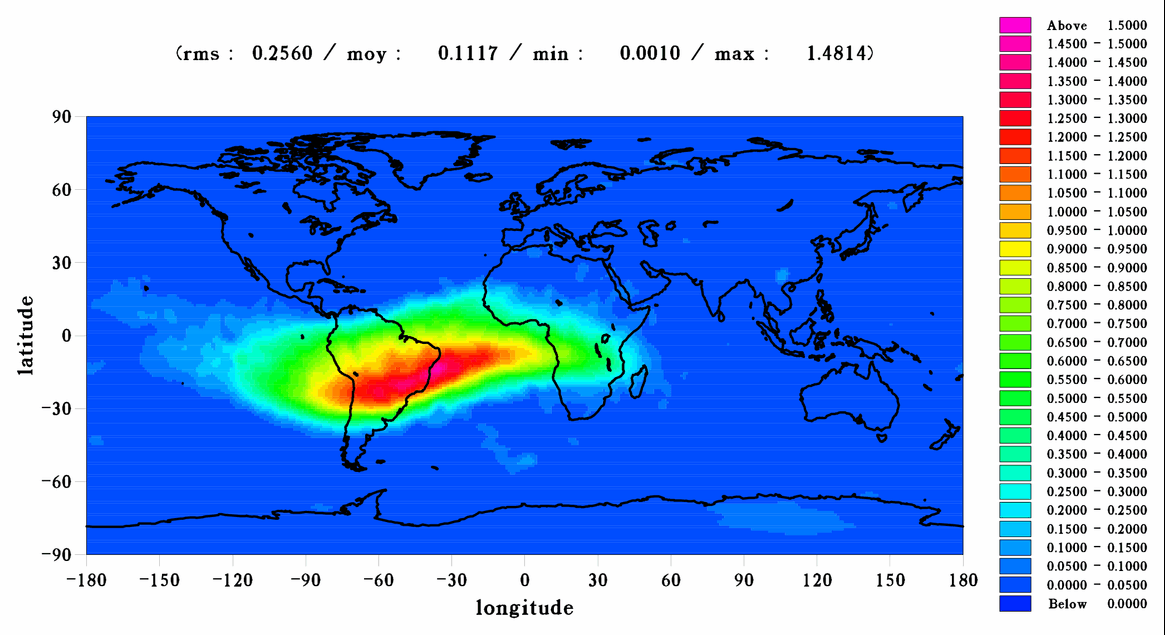
South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA)
The SAA is a region of space with an enhanced concentration of ionizing radiation due to the configuration of the Earth’s magnetic field. Such radiation can damage spacecraft electronics and cause Single Event Upsets (SEU), which can impair the functioning of electronic components.
The SAA Transit component also computes the energy flux and/or flux contour of SEU relative probability for altitudes between 400 and 1500 km. The model of the SAA is based on data received from the Compact Environment Anomaly Sensor (CEASE) detector flown on the Tri-Service Experiment (TSX-5) satellite during the epoch 2000 – 2006.